
In antiquity, Homer's authorship of the poem was not questioned, but contemporary scholarship predominantly assumes that the Iliad and the Odyssey were composed independently and that the stories formed as part of a long oral tradition. The Odyssey was originally composed in Homeric Greek in around the 8th or 7th century BC and, by the mid-6th century BC, had become part of the Greek literary canon.

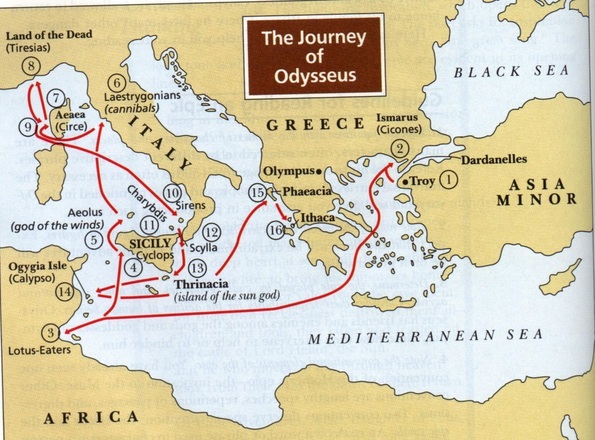
In his absence, Odysseus was assumed dead, and his wife Penelope and son Telemachus had to contend with a group of unruly suitors who were competing for Penelope's hand in marriage. After the war, which lasted ten years, his journey lasted for ten additional years, during which time he encountered many perils and all of his crewmates were killed. It follows the Greek hero Odysseus, king of Ithaca, and his journey home after the Trojan War. As with the Iliad, the poem is divided into 24 books.

It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. The Odyssey ( / ˈ ɒ d ɪ s i/ Ancient Greek: Ὀδύσσεια, romanized: Odýsseia) is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. 15th-century manuscript of Book I written by scribe John Rhosos ( British Museum)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
